The concept of Market Pull propels businesses towards customer-centric success. Beyond the confines of traditional supply-driven models, market pull embodies a strategic shift, where consumer needs and desires drive product development.
Understanding Market Pull
Market pull occurs when consumers naturally desire a product as soon as they become aware of it, and they are ready to take any necessary steps to acquire it. This phenomenon is the driving factor behind achieving “product-market fit.”
In simpler terms, having market pull means that the market eagerly embraces your idea as you introduce it, and you don’t struggle to sell it; rather, the demand spontaneously emerges.
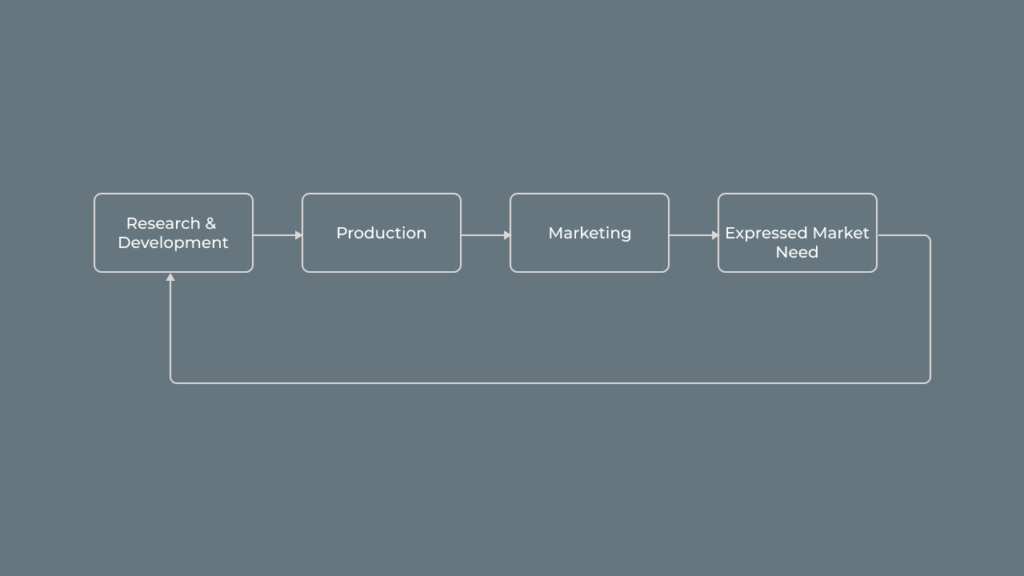
Unlike the classic product development approach which is centred around pushing novel technology then educating the market of its value, market pull uses the expressed, unmet need of the market as a signal to product development. This results in 3 behaviours from the target audience when they encounter the product:
Understanding
Consumers inherently recognize the worth of a product without requiring a detailed breakdown of its features. This reduces the necessity for prolonged sales efforts.
Appreciation
Consumers can easily justify the effort, cost, and potential risk of transitioning to the product.
Excitement
Consumers eagerly desire the product without delay. This strong eagerness aids them in overcoming the obstacles associated with switching.
Advantages of Market Pull
When developing your product, it’s important you pay attention to the existence of market pull or not. There are vital advantages your product stands to benefit from if it has market pull
Low to Moderate Cost of Risk
Products with market pull tend to exhibit a lower to moderate cost of risk due to their inherent consumer demand and strong value proposition. Because these products are intuitively valued by consumers and offer perceived benefits that justify their adoption, the risk of low demand or customer dissatisfaction is reduced. Consumers are enthusiastic about these products, leading to quicker adoption and reducing the uncertainty associated with higher risk products. This dynamic translates to a more stable demand and a decreased likelihood of significant financial losses, resulting in a manageable cost of risk for businesses.
Low to Moderate Cost of R&D
The cost of Research and Development (R&D) for products with market pull is low due to their well-defined demand and customer-driven nature. Since these products cater to existing consumer needs and preferences, businesses can focus R&D efforts more precisely, avoiding extensive experimentation and iteration. Such products align with known market trends, thereby reducing the risk of costly failures. This targeted approach streamlines the R&D process, and fosters efficient resource allocation. As a result, the cost of R&D remains manageable, and businesses can effectively meet consumer demands while maintaining a competitive edge.
Easy Marketing
The strong alignment of with existing consumer desires makes such products easy to market. These products are designed to fulfil specific needs or solve well-recognized problems. Additionally, consumer enthusiasm for such products generates organic word-of-mouth promotion, leveraging the power of customer advocacy. This direct connection to consumer demand simplifies marketing strategies, allowing businesses to focus on highlighting benefits and addressing consumer pain points.
Some Proven Examples of Market Pull
Majority of successful startups have one thing in common: market pull. Market pull can be leveraged in various ways. This is why we’ve grouped the successful examples according to the market pull strategy that was leveraged by the companies. These categories showcase how products aligned with inherent desires can generate market pull and inevitably emerge victorious
Unlocking Investment Potential
The power of market pull becomes evident when investment opportunities are democratised. This phenomenon occurs as previously untapped asset classes, such as startups, become accessible to investors who sought their potential but were previously excluded. By fulfilling this existing demand, a surge of capital flows in—a quintessential case of market pull. The dynamic exemplifies the allure of catering to latent desires and benefiting from a scarcity-driven surge in demand.
Republic is a great example of a startup leveraging this market pull strategy. The startup makes investing possible for investors who can’t pass the accreditation phase due to their low salaries or net worth.
Expanding Income Horizons
Introducing new income avenues can trigger a remarkable instance of market pull. When individuals are empowered to generate substantial earnings with minimal prerequisites, it appeals to the vast number of individuals seeking supplementary income sources. This magnetic effect, known as market pull, is ignited as the product aligns precisely with the widespread aspiration for enhanced financial prospects, leading to a surge in demand.
Uber is a successful startup that introduced an income avenue for car owners through ride sharing.
Streamlining Efforts and Costs
Another proven way to leverage market pull is by developing products that eliminate extensive labour at a relatively low cost. By doing this, you’re helping your target audience reduce their overhead, in terms of hands and cost. The advantage of products like these over existing solutions is their low learning curve. This makes it possible for anyone with little or no related skill set to achieve results usually afforded to professionals.
Canva is a startup that leverages this market pull strategy. With Canva, consumers with little or no knowledge of graphic design can now create appealing designs within a short period and at a low cost. This is in contrast with incumbent tools like Adobe Photoshop which requires the pricey Adobe Creative Cloud licence and proficiency in graphic design.
Enhancing Affordability and Convenience
Market pull can be activated through a combination of affordability and convenience. When sought-after products experience a notable price reduction without compromising quality, it can ignite a market pull effect. The pull becomes even stronger when these new products offer enhanced convenience alongside cost savings. The element of convenience plays a pivotal role, as it assists consumers in rationalising the effort involved in transitioning to the new product, thus bolstering the appeal and uptake.
Coursera and Spotify are proven examples of startups employing this market pull strategy. They provide educational and entertaining content to the market in a seamless manner, without perverting the quality of the content.
Conclusion
There are definitely more strategies besides the aforementioned ones for achieving market pull. A great rule of thumb for assessing if your product has market pull is to answer the question: Can consumers easily grasp the value of my product without much explanations? The power of market pull lies in aligning offerings with genuine market needs. This enhances the odds of success for a business.
- Creating Information Architecture (IA) for Mobile Applications - October 2, 2021
- What is Market Pull? Some Proven Examples - September 4, 2021
- What is Competitive Advantage? Types and Examples - August 9, 2021